Get a Brief Idea about SQL Server Database Auditing
Auditing in general refers to a process of tracking or monitoring the changes that have taken place in a system. Now the question is why do we require auditing and what relation does it have with SQL Server? For a person who has been working for long with SQL Server would really like to know the answers for the above question. Hence, we proceed with the basics of auditing and how did it come into existence with SQL Server.
Let us have an overview of what we are going to discuss on this page.
Importance of Auditing
The logical question is what you need to audit .From a security viewpoint, auditing became essential to track the activities of a person working in a system. Various malicious activity that affects the system has given rise to the need of auditing. It cannot be used to prevent any activity but yes, you can review the actions that have occurred in the system and it will give you an insight of what all actions has occurred and who has conducted them.
Auditing as a concept has existed theoretically but practically, it is the next difficult task because it requires the implementation of customized solutions and extensive resources and time involvement
Introduction to Auditing in SQL Server 2005
SQL server auditing can be confusing because the term audit can be used in many contexts. However, over here, it refers to following of set of practices for tracking the changes or activities that takes place on SQL server. Auditing logs user actions at the server or database level. Complete record of who is doing what and what they are doing to SQL server. It could range from logging and connection attempts to SQL server. You can describe SQL Server auditing, as a brief audit of what type of objects is users accessing in an organization.
How Was Auditing Done in SQL Server 2005
Auditing in SQL server 2005 was carried out with a combination of tools. The auditing feature allowed administrators to execute auditing at two levels
- According to the requirements of data security
- According to C2 security requirements
Auditing was done with SQL trace /profiler using API of stored procedures. The SQL profiler is a utility for tracing the events that occur on SQL server. Then it saves that information in the tables or in the form of files that have the extension as .TRC .However, it failed to fulfil some of the basic criteria that was required in an organization. It had the following limitations.
- Extended no support of the management tools
- Incapable of fine-grained auditing
- Involved lot of overheads
To remove the discrepancies associated with the auditing in SQL Server 2005, a new auditing feature was introduced with the SQL Server 2008 R2. Let us get an idea about it.
Introduction to Auditing in SQL Server 2008 R2
Before understanding the auditing feature in SQL server 2008, we first need to find out the reason for its introduction. As a part of risk analysis and assessment strategy, data protection became one of the concern for organization implementing SQL server and the need for following requirements were identified
- Personal Identifiable information
- For regulatory Compliance
- To conduct data security strategy
- Tracking the usage of confidential information
The answer came by introducing the SQL server 2008 R2 came up with a new concept of auditing altogether addressing the mechanism of auditing with four basic goals. Designed to meet the challenges in the areas of security, performance, manageability and discoverability, SQL Server 2008 R2 provided the granular level of auditing that did not exist in SQL server 2005.
Features of SQL server 2008 Auditing
- Involves fine grain auditing of data definition languages & Data manipulation Languages
- Integrated with the policy based management
- Auditing of various activities in a database
- Operates within the SQL Server Engine
- Introduces auditing at database level and at server level
To understand the auditing process in SQL server, let us go through the systematic procedure of creating audits.
Demonstration of SQL Server Database Auditing in SQL Server 2008
The basic process for creating SQL server 2008 R2 auditing is given below
#Creation of Audit Package
An audit package states the properties of audit and directs the information that has been captured to be saved in the destination location. To access the audit packages
Move to security<<Audits
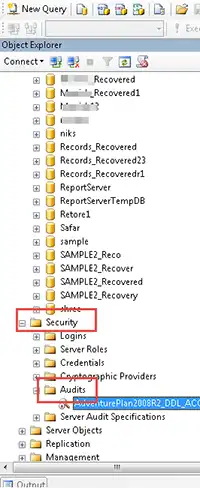
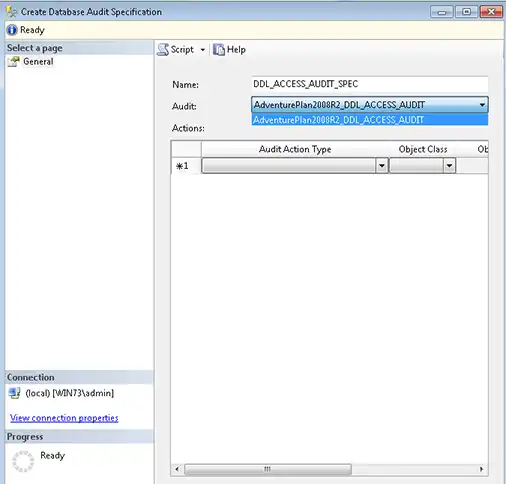
#Creation of Database Audit Specification
Database audit specification records all the events at database level involving database objects. Here, database events include DDL/DML statements like SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE and INSERT. The database audit specification is carried out through SSMS (SQL Server Management Studio).
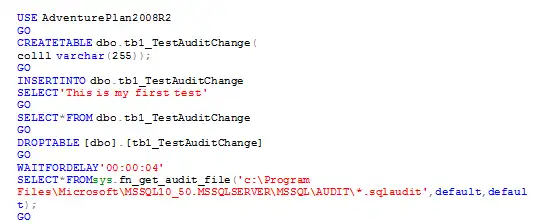
The following code will create database audit specification on the Adventure Plan2008R2 database
#Enabling The Audit Specification
Finally, you need to enable the database audit specification. This is done by navigation to the following settings
Database Audit Specifiaction<<Right click on the DDL_ACCESS_AUDIT_SPEC<<Enable Datbase Audit Specification
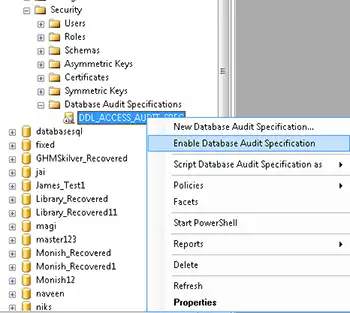
Once you enable the database audit specifiaction , you get a message displayed below
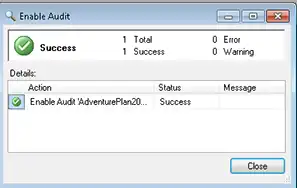
#Querying The Created Audit File
The function that is used for querying the audit file is given below
fn_get_audit_file
The SQL query for returning the data that has been audited is gioven in the following manner
![]()
#Analyzing the Audits That Has Been Captured
To view the audit logs that have been created, right click on the AUDIT file, and then select the option ’View Audit logs’.
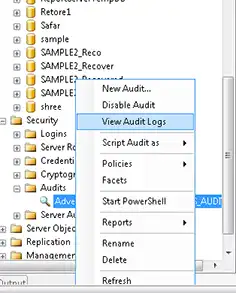
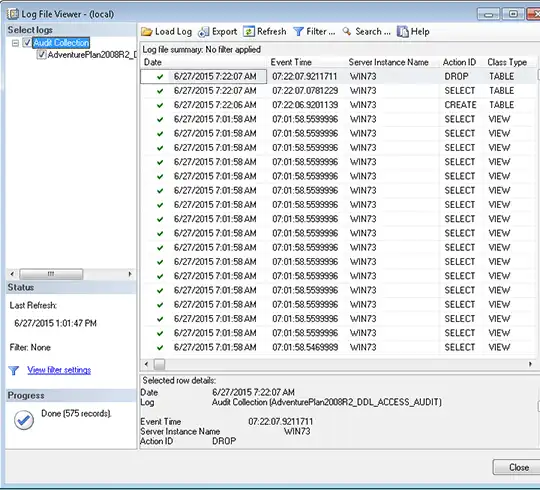
This will open the window of SQL log viewer. Here, you can analyze all the log files and track the activities of a person.
Conclusion
SQL Server Database auditing has gained a new momentum in data forensics .Reason being the availability of log files has given a new dimension to the investigation procedure where forensic experts rely on effective presentation of evidence. By exporting the logs to a suitable platform, the forensic investigators can analyze them effectively.

