Overview of BitLocker Encryption in Windows Systems – Complete Guide
When it comes to data security and protection, especially within the Windows system, BitLocker plays a crucial role. In this article, we’ll explore BitLocker, what is it, and its significance. Here you’ll also find insights on the role of BitLocker in digital forensics.
So, without further ado, let’s first understand its meaning.
What is BitLocker?
It is a security feature found in Windows systems that provides encryptions for entire volumes. The primary function of this technology is to encrypt entire drives or volumes, rendering the data stored on them inaccessible to unauthorized users. It implements strong encryption algorithms and secure key management to safeguard sensitive information. In other words, evenif the device is lost or stolen, the data remains confidential.
This security feature in the Windows system is valuable to individuals as well as organizations who want their data to be protected from potential threats and breaches.
Now, let’s get familiar with the meaning of different icon adornments for hard drives that appear in ‘This PC’.
What Do The Hard Drive Icons Mean in Windows System?
Before explaining, first, glance through the image given below.
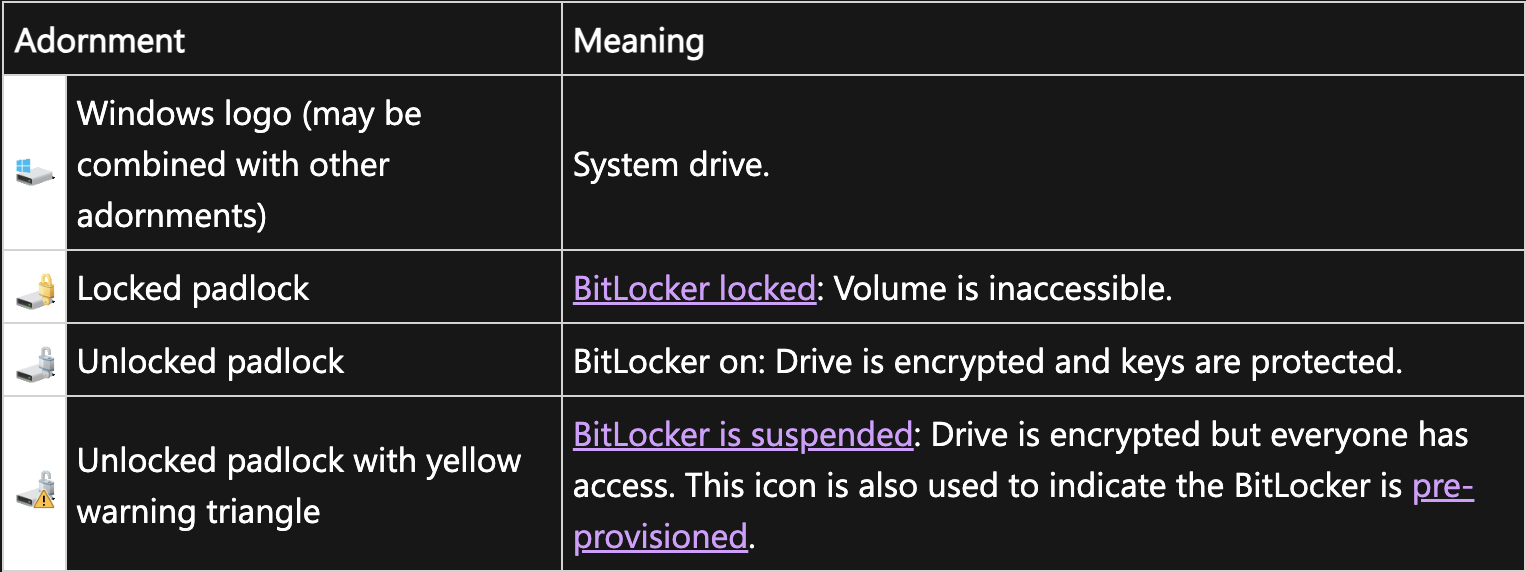
Let’s cover the icons one by one.
- Windows Logo – It is the System Drive, the primary storage device where the Windows operating system and necessary system data are installed. This is frequently identified by the Windows logo. It acts as the OS’s core hub, allowing the machine to start up, run, and display the recognizable Windows user interface.
- Locked Padlock – A locked padlock is a symbol of security and privacy. It signifies that access is restricted and protected, ensuring the safety of what is enclosed or safeguarded behind it.
- Unlocked Padlock – This icon signifies BitLocker on, the Drive is encrypted and keys are protected.
- Unlocked Padlock with Yellow Warning Triangle – It denotes suspend BitLocker. In this case, the Drive is encrypted but everyone has access. BitLocker suspension does not imply that BitLocker decrypts the volume’s contents. Suspension, on the other hand, makes the key needed to decode the data publicly available. The disc is still encrypted when new data is written to it.
What is the Role of BitLocker in Digital Forensics?
In the context of digital forensics, BitLocker plays a dual role. On one hand, it is a valuable tool for protecting data and maintaining the confidentiality of information. On the other hand, it presents challenges and opportunities for forensics analysts when they need to access and analyze data on BitLocker-encrypted drives.
Here is the dual role of BitLocker explained in the below points.
- Data Protection: The fundamental purpose of BitLocker is to encrypt data on discs so that it is safe and private. It is quite difficult for unauthorized people to access or steal important information thanks to this encryption. This degree of security can be a barrier in the context of digital forensics when attempting to access a suspect’s data for investigative purposes.
- Legal and Ethical Considerations: When working with BitLocker-encrypted discs, digital forensics specialists need to follow legal and ethical guidelines. They must respect people’s right to privacy and obtain the appropriate authorization. Following the right legal channels and due process are necessary in order to gain access to BitLocker-protected data.
- Decryption and Analysis: Forensics investigators might require the decryption key or password in order to examine data on a BitLocker-encrypted device. After decrypting the drive with the right credentials, they can examine the contents using forensic software like FTK (Forensic Toolkit) or other specialized tools. Examining documents, emails, web logs, and any other digital artifacts that might be pertinent to the inquiry are all included in this process.
- Evidence Recovery: When BitLocker is set up and maintained correctly, it creates a digital trail of its actions. Usage logs and recovery keys are part of this. These traces can be used by forensic experts to prove when a BitLocker-protected drive was last accessed or whether BitLocker was enabled on a certain system.
- Challenges: In digital forensics, BitLocker might present difficulties because it can be challenging to obtain the password or encryption key, particularly when dealing with uncooperative or inattentive people. In order to retrieve evidence, investigators must apply cutting-edge methods, work with computer security specialists, and make use of proprietary equipment.
Overview of FTK and BitLocker in Digital Forensics
Forensic Toolkit, sometimes known as FTK, is a digital forensics software program. Mostly, investigators and forensic specialists use this to examine and retrieve digital evidence from computers and other digital devices. In contrast, BitLocker is a disc encryption tool that comes pre-installed on some Microsoft Windows operating systems. There are several methods that FTK can be applied to BitLocker-encrypted drives in digital forensics:
- BitLocker Recovery Key: BitLocker encrypts a drive’s contents, making it impossible to access the data without an encryption key. If the password or BitLocker key is known, FTK can be utilized in a forensic investigation to access and examine the decrypted data on the BitLocker-protected drive.
- Decryption of BitLocker Keys: If forensic investigators possess the necessary legal authorization, they can utilize FTK to carry out a decryption of BitLocker keys in situations where the password or key is unknown. Investigators can examine the data in a more readable format since FTK can handle decryption if the required keys or credentials are present.
- Data acquisition and analysis from BitLocker-protected drives can be done with FTK. Sometimes, forensic specialists will make a forensic image of the encrypted drive, which they can subsequently process and analyze utilizing File Transfer Protocol (FTP).
- Keyword Research and Analysis: FTK has strong search and analysis features that can assist investigators in finding pertinent data inside BitLocker-protected files. This involves looking for other digital artifacts, file metadata, and keywords.
Conclusion
We can conclude that BitLocker encryption serves as a defense mechanism to protect sensitive data maintaining its confidentiality. Its role in digital forensics emphasizes the challenges investigators encounter. It also presents opportunities to access and analyze encrypted data. This underscores the delicate balance between data security and effective investigative processes. In other words, it requires an essential balance between data security and the need for effective investigative processes.

